Votre panier est vide.
Bookkeeping
What Is a Solvency Ratio, and How Is It Calculated?
Liquidity in accounting refers to a company’s ability to pay its liabilities as due, in a timely manner. As an investor, you would certainly want to assess a firm’s liquidity ratios as well as its solvency ratios which are important parameters to give a go-ahead for an investment decision. Solvency vs. liquidity is essentially a long-term vs. a short-term lack of long-term solvency refers to: analysis of a company’s strength. With solvency, you’re assessing how well the company can continue operating into the future. With liquidity, you’re assessing how well the company can run its operations in the short term. Short-term solvency usually focuses on the amount of cash and current assets that can be used to cover obligations.

About The Motley Fool
- Pay particular attention to negative outliers to check if they are the result of a one-time event or indicate a worsening of the company’s fundamentals.
- There are several ways to figure a company’s solvency ratio, but one of the most basic formulas is to subtract their liabilities from their assets.
- Moreover, a sustainable approach to business can prevent solvency issues and safeguard against the outcomes when a company lacks financial solvency.
- The interest coverage ratio measures the company’s ability to meet the interest expense on its debt, which is equivalent to its earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT).
- The shareholders’ equity on a company’s balance sheet can be a quick way to check a company’s solvency and financial health.
This balance between debt and capital is critical—too much debt may compromise a company’s solvency, while ample capital usually indicates robust financial footing. As such, companies strive to maintain a solvency ratio that demonstrates immediate liquidity, long-term fiscal responsibility, and resilience. This ratio measures the ability of a company to cover its debt obligations with its assets after all liabilities have been satisfied. It’s usually calculated by dividing the value of a firm’s tangible assets by its outstanding debt obligations. Financial solvency refers to a company’s ability to meet its long-term financial obligations and is crucial for maintaining stability and trust among stakeholders. But it’s not simply about a company being able to pay off the debts it has now.
- By measuring solvency in both of the ways described above, you can get a better picture of the company’s overall health.
- It indicates that a business has more assets than liabilities, ensuring it can continue operations without the risk of bankruptcy or financial distress.
- Therefore, managing solvency ratios involves a delicate balance amid equity, assets, and debts, a task that any prudent business, such as Sunwise Capital, navigates with strategic focus.
- The financial leverage ratio indicates the degree to which a company utilizes borrowed funds.
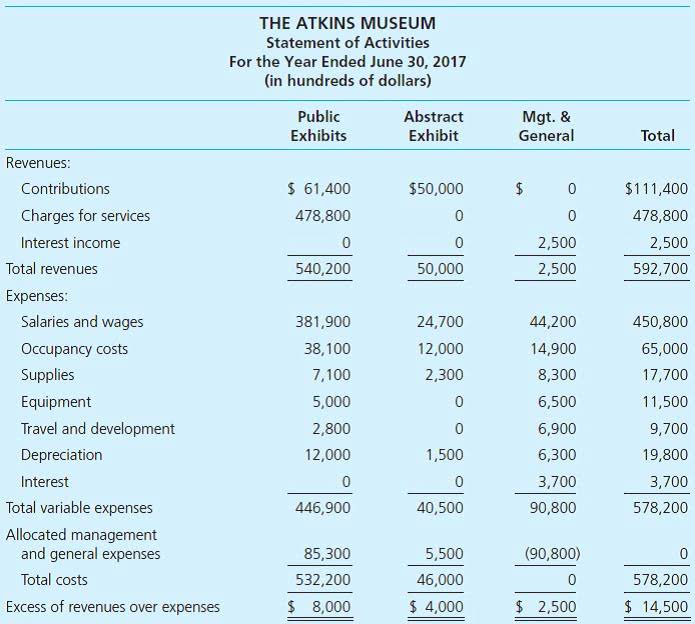
- Overall, the financial ratios suggest that BJ Appliances has a moderate level of solvency.
- The current ratio measures a company’s ability to pay off its current liabilities (payable within one year) with its current assets such as cash, accounts receivable, and inventories.
Equity Ratio

An over-reliance on debt can jeopardize solvency, tipping the scales unfavorably. A company that is insolvent or is only barely solvent and that has poor liquidity is in a weak position. The first, as noted above, is a company’s cash or cash-equivalent assets it has on hand. These are assets that the business https://www.bookstime.com/articles/suspense-account could reliably sell within a short period without taking a significant loss. Financial assets like stocks are considered highly liquid because they’re designed for quick sales while retaining their value. On the other hand, capital assets like real estate are not considered part of a liquidity calculation.
Discover The 5 Financial Solvency Secrets
There are also other ratios that can help to more deeply analyze a company’s solvency. The interest coverage ratio divides operating income by interest expense to show a company’s ability to pay the interest on its debt. The debt-to-assets ratio divides a company’s debt by the value of its assets to provide indications of capital structure and solvency health. When a company can no longer meet its financial obligation that company has become insolvent. This often leads to insolvency proceedings in which legal action is taken to liquidate a company’s assets to pay down its debt. The AFSA offers a way to compare options and check eligibility if you need to.

It’s important to look at a variety of ratios to comprehend the true financial health of a company, as well as understand the reason that a ratio is what it is. A company needs to be compared to its peers, particularly the strong companies in its industry, to determine if the ratio is an acceptable one or not. The relationship between the total debts and the owner’s equity in a company. The solvency of a business is assessed by looking at its balance sheet and cash flow statement. There are several ways to figure a company’s solvency ratio, but one of the most basic formulas is to subtract their liabilities from their assets. If there is still value after the liabilities have been subtracted, the company is considered solvent.
The calculation divides a company’s net operating income by its total debt service costs. A DSCR greater than 1 means the company has sufficient income to pay its debts. Therefore, managing solvency ratios involves a delicate balance amid equity, assets, and debts, a task that any prudent business, such as Sunwise Capital, navigates with strategic focus.